Purposes
This research explores the game-based intelligent test (GBIT), predicts the possibilities of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores and the risk of cognitive impairment, and then verifies GBIT as one of the reliable and valid cognitive assessment tools.
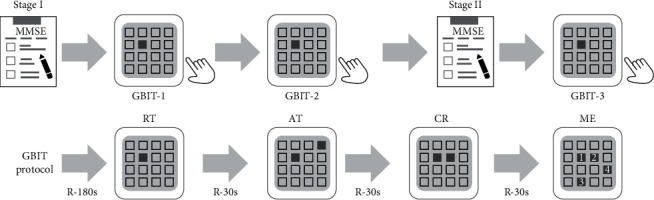
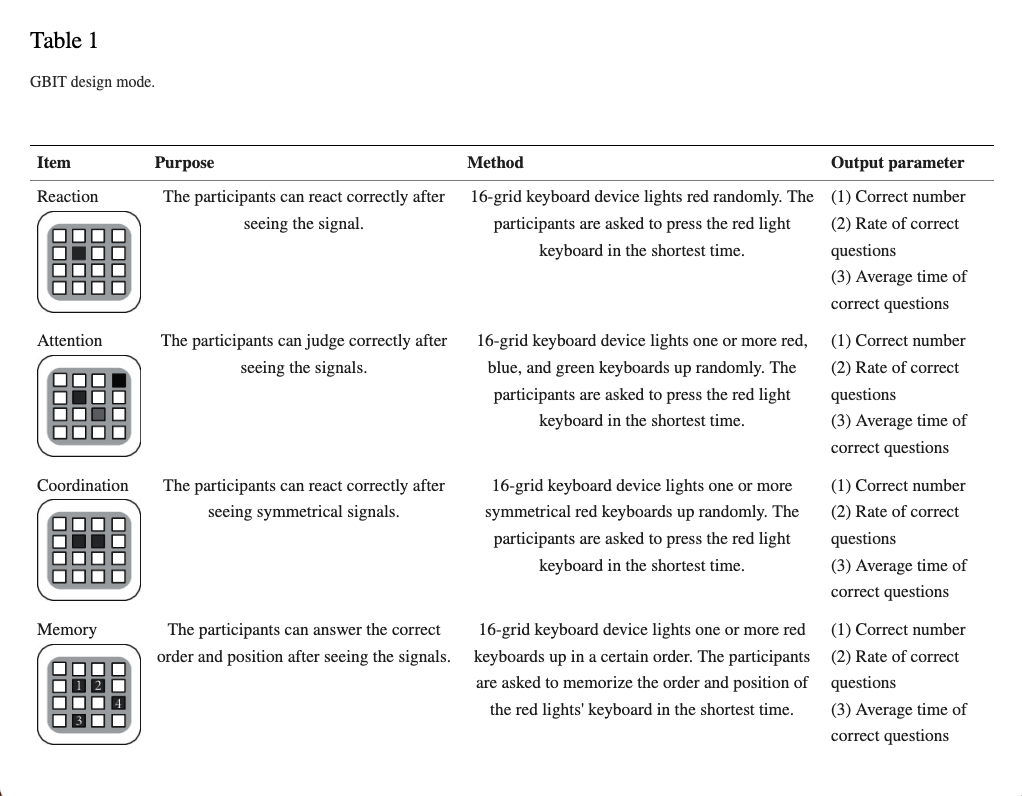
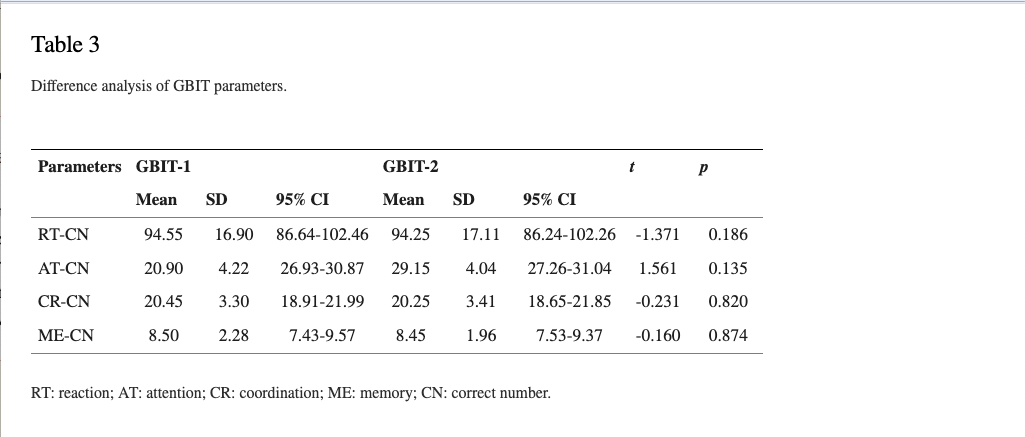
Experimental design diagram. The study was divided into two stages. In the first stage, 20 recruited participants were assigned to do the MMSE questionnaire, followed by the GBIT-1 test. They did the second GBIT-2 test after one month. The experiment’s purpose of the first stage is to confirm the reliability of GBIT. In the second stage, 117 elderly participants did the MMSE questionnaire and then the GBIT for the study. The GBIT process is a three-minute quiet rest, followed by reaction (RT) for two minutes, attention (AT) for two minutes, coordination (CR) for two minutes, and finally memory (ME) for four minutes. The participants had a 30-second rest between the tests.
Methods
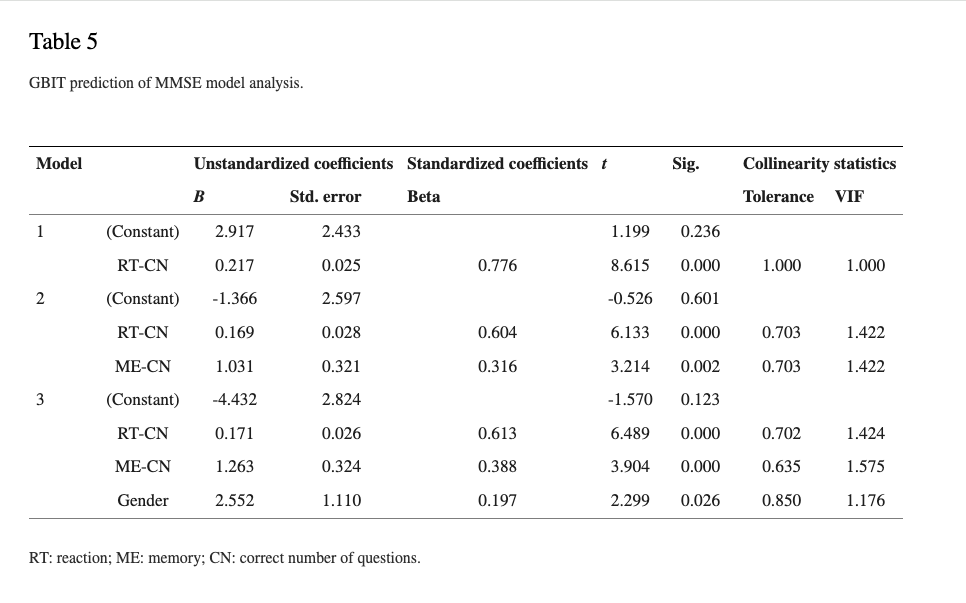
This study recruited 117 elderly subjects in Taiwan (average age is 79.92 ± 8.68, average height is 156.91 ± 8.01, average weight is 59.14 ± 9.67, and average MMSE score is 23.33 ± 6.16). A multiple regression model was used to analyze the GBIT parameters of the elderly’s reaction, attention, coordination, and memory to predict their MMSE performance. The binary logistic regression was then utilized to predict their risk of cognitive impairment. The statistical significance level was set as α = 0.05.
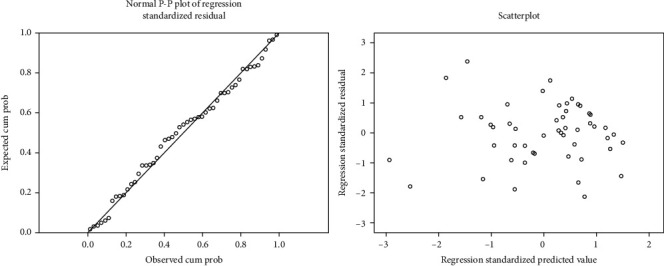
The forecasting models of normal error hypothesized diagnosis analysis.
Results
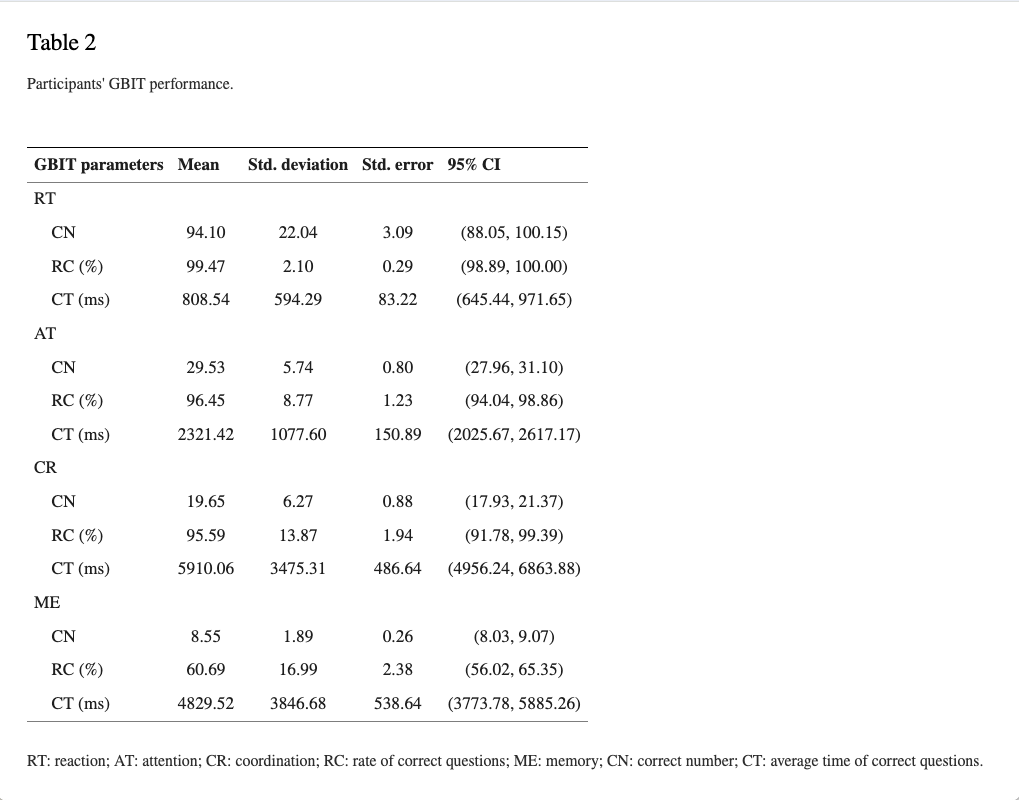
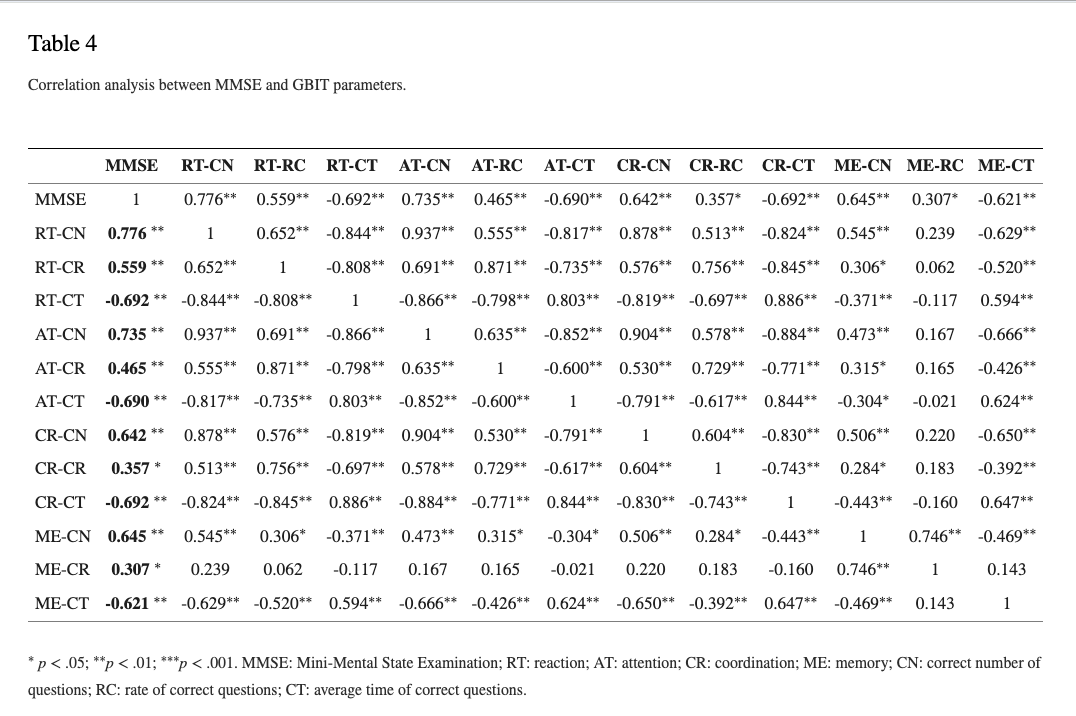
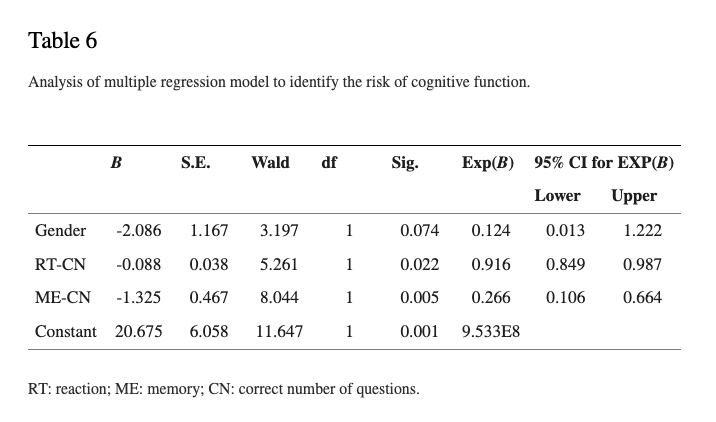
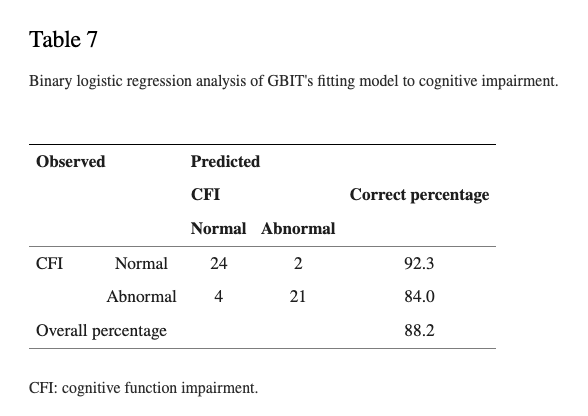
Multiple regression analysis showed that gender, the correct number of reactions, and the correct number of memory have a significantly positive predictive power on MMSE of the elderly (F = 37.60, R2 = 0.69, and p < 0.05). Binary logistic regression analysis noted that the correct average number of reactions falls by one question, and the ratio of cognitive dysfunction risk increases 1.09 times (p < 0.05); the correct average number of memory drops by one question, the ratio of cognitive dysfunction risk increases 3.76 times (p < 0.05), and the overall model predictive power is 88.20% (sensitivity: 84.00%; specificity: 92.30%).

GBIT predicts the probability of cognitive dysfunction. RT-CN is the probability chart of the correct number of reactions predicting cognitive dysfunction (fixed RT-CN = average value). ME-CN shows the probability of the correct number of memory predicting cognitive dysfunction (fixed ME-CN = average value). The black curve is male, and the gray curve is female. The performance trends of different genders are the same. The more questions answered correctly, the lower is the risk of cognitive dysfunction.
Conclusions
This study verifies that GBIT is reliable and can effectively predict the cognitive function and risk of cognitive impairment in the elderly. Therefore, GBIT can be used as one of the feasible tools for evaluating older people’s cognitive function.
___
Citation Source:
Lin CW, Mao TY, Huang CF. A Novel Game-Based Intelligent Test for Detecting Elderly Cognitive Function Impairment. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 29;2021:1698406. doi: 10.1155/2021/1698406. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9858529. doi: 10.1155/2023/9858529. PMID: 34880929; PMCID: PMC8648469.
